This critical financial metric is vital for accurately assessing product costs or services. As you’ve learned, understanding the cost needed to manufacture a product is critical to making many management decisions (Figure 6.2). Knowing the total and component costs of the product is necessary for price setting and for measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization. Remember that product costs consist of direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. By using the predetermined rate product costs and therefore selling prices can be calculated quickly throughout the year without the need to wait for actual overheads to be determined and allocated. In addition while manufacturing overheads might vary seasonally throughout the year, the use of a constant predetermined rate avoids a similar variation in unit product cost.
How to calculate the predetermined overhead rate: Example 3
So, it may not be a good idea with perspective to effective business management. Suppose following are the details regarding indirect expenses of the business. Once costs are broken down, small businesses can assess if any categories are excessive. For example, upgrading to energy-efficient equipment could reduce utilities.
Company
Enforcing company-wide cost-saving policies around printing, travel, etc. further helps minimize overhead. This comprehensive guide breaks down overhead rate calculation into clear, actionable steps any business can follow. Conversely, the cost of the t-shirts themselves would not be considered overhead because it’s directly linked to your product (and obviously changes based on the volume of products you create and sell). A high overhead rate can indicate that you need to control your costs better or raise your prices.
- So, a more precise practice of overhead absorption has been developed that requires different and relevant bases of apportionment.
- On the other hand, the business with the machine incentive environment absorbs overhead based on the machine hours.
- In order to estimate the predetermined overhead rate it is first necessary to to decide on an activity base on which to apply overhead costs to a product.
- A predetermined overhead rate is an allocation rate that is used to apply the estimated cost of manufacturing overhead to cost objects for a specific reporting period.
- Company B wants a predetermined rate for a new product that it will be launching soon.
Understanding Goodwill in Balance Sheet – Explained
These two factors would definitely make up part of the cost of producing each gadget. Calculation of predetermined overhead rates enables manufacturers to set product prices that accurately reflect the production costs, safeguarding profit margins. By inputting basic cost and activity data, Sourcetable’s AI assistant instantly computes the overhead rate using the formula Total Estimated Overhead Costs / Total Estimated Allocation Base.
Company X and Company Y are competing to acquire a massive order as that will make them much recognized in the market, and also, the project is lucrative for both of them. After going to its terms and conditions of the bidding, it stated the bid would be based on the overhead rate percentage. Therefore, the one with the lower shall be awarded the auction winner since this project would involve more overheads. Use the following data for the calculation of a predetermined overhead rate. Therefore, this predetermined overhead rate of 250 is used in the pricing of the new product. The overhead rate affects pricing by showing how much you need to cover your costs.
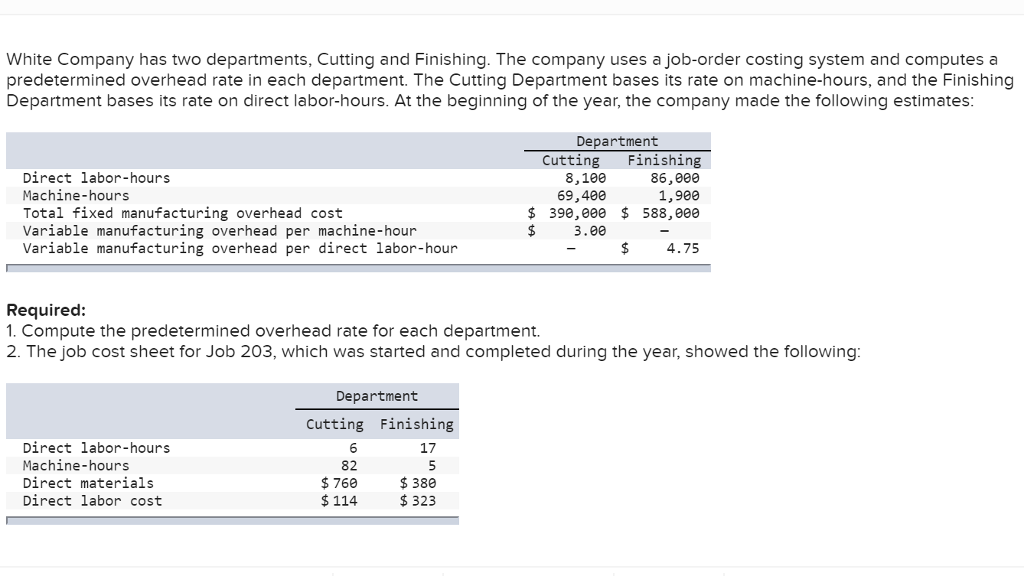
Product costing can be extremely helpful in managerial decision-making, and its prime use is related to product costing and job order costing. So, it’s advisable to use different absorption bases for the costing in terms of accuracy. The business is labor-intensive, and the total hours for the period are estimated to be 10,000.
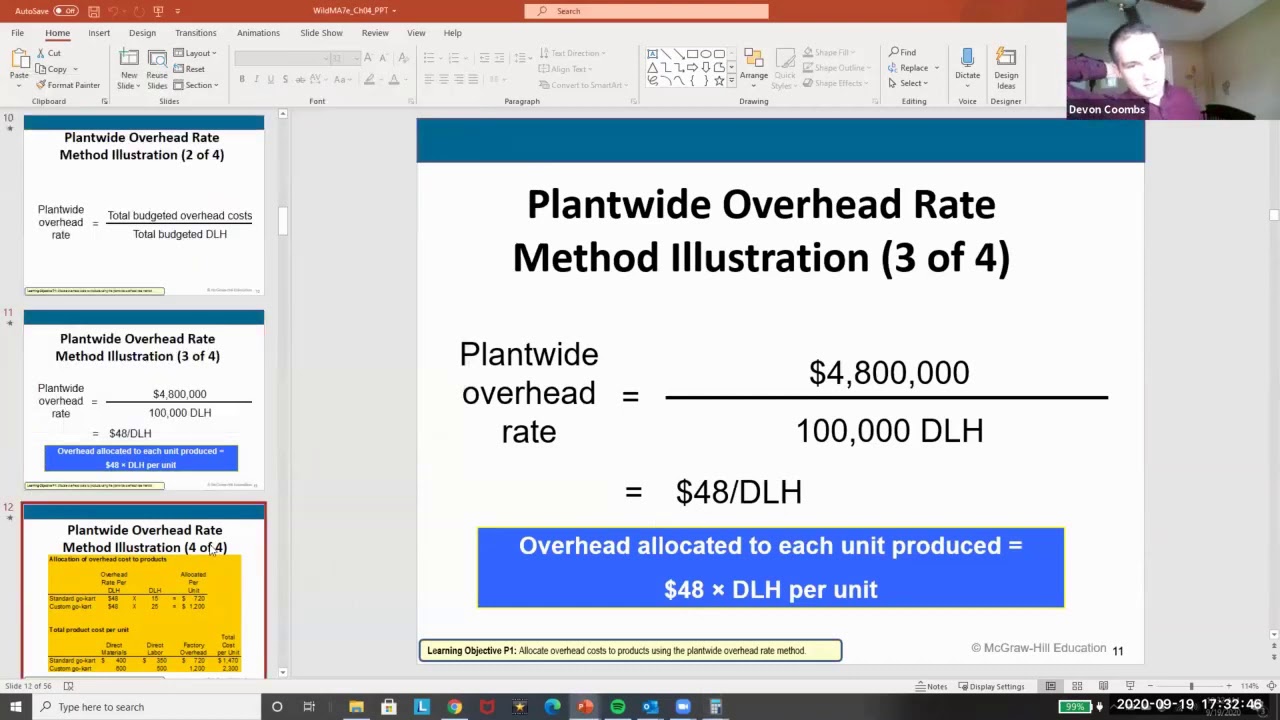
The allocation base could be direct labor costs, direct labor dollars, or the number of machine-hours. The company would then estimate what the predetermined overhead cost would be and divide them to determine what the manufacturing overhead cost would be. The predetermined overhead rate is calculated by dividing the estimated manufacturing overhead by the estimated activity base (direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, or machine hours). For instance, if the activity base is machine hours, you calculate predetermined overhead rate by dividing the overhead costs by the estimated number of machine hours. This is calculated at the start of the accounting period and applied to production to facilitate determining a standard cost for a product.
On the other hand, a low overhead rate might show that you are operating efficiently. If the actual overhead at the end of the accounting period is 1,575 the overhead is said to be under applied by 125 (1,450 – 1,575). If the actual overhead at the end of the accounting period is 1,575 the overhead is said to be over applied by 25 (1,600 – 1,575).
This rate also helps to determine when it’s time to review the company’s spending to protect its profit margins. Keep reading the article to learn more about the predetermined overhead rate and how to calculate and apply it. The first step is to estimate total overheads to be incurred by the business. This can be best estimated by obtaining a break-up of the last year’s actual cost and incorporating seasonal effects of the current period. The business has to incur different types of expenses for the manufacturing of the products. These expenses include direct material, direct labour, direct overheads, and indirect overheads etc.
At the end of the accounting period, the actual indirect cost is obtained and compared with the absorbed indirect. Larger organizations may employ a different predetermined overhead rate in each production department, which tends to improve the accuracy of overhead application by employing a higher level of precision. However, the use of multiple predetermined overhead rates also increases the amount of required accounting labor. A predetermined overhead rate is a useful tool for businesses of all sizes. By understanding how to calculate this rate, business owners can better control their overhead costs and make more informed pricing decisions.
It is applied for the absorption of overheads during the period for which they have been computed. A number of possible allocation bases are available for the denominator, such as direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, and machine hours. Finally, if the business uses material costs as the activity base and the estimated material costs for the year is 160,000 then the predetermined manufacturing how to calculate predetermined overhead rate overhead rate is calculated as follows. If a job in work in process has recorded actual machine hours of 140 for the accounting period then the predetermined overhead applied to the job is calculated as follows. If a job in work in process has recorded actual labor costs of 6,000 for the accounting period then the predetermined overhead applied to the job is calculated as follows.
